Solutions
There is no perfect ground improvement solution that fits every soil or project. Our challenge is to provide custom made foundation and soil improvement solutions that meet our clients Budget, Schedule and Quality Standards.
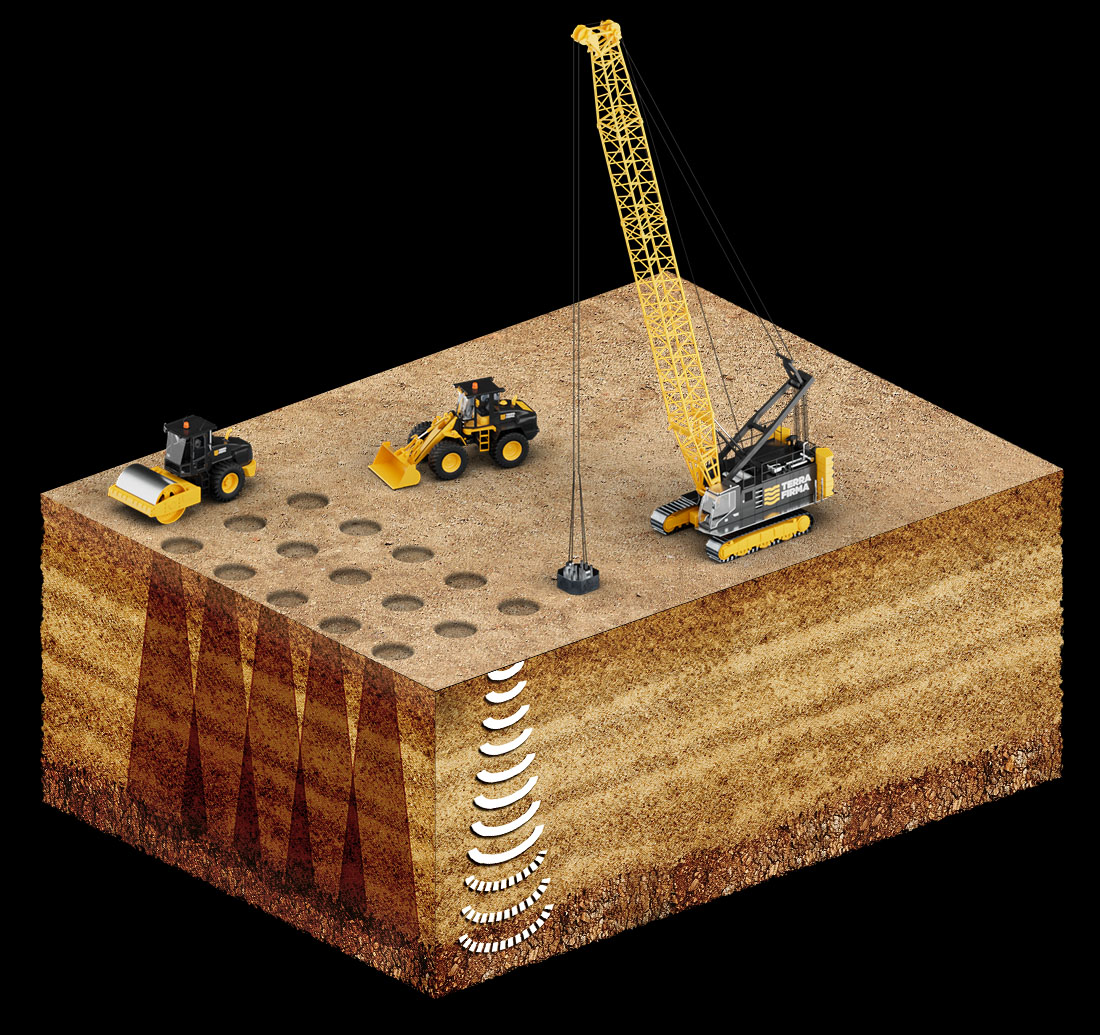
Dynamic Compaction (DC)
Dynamic Replacement (DR)

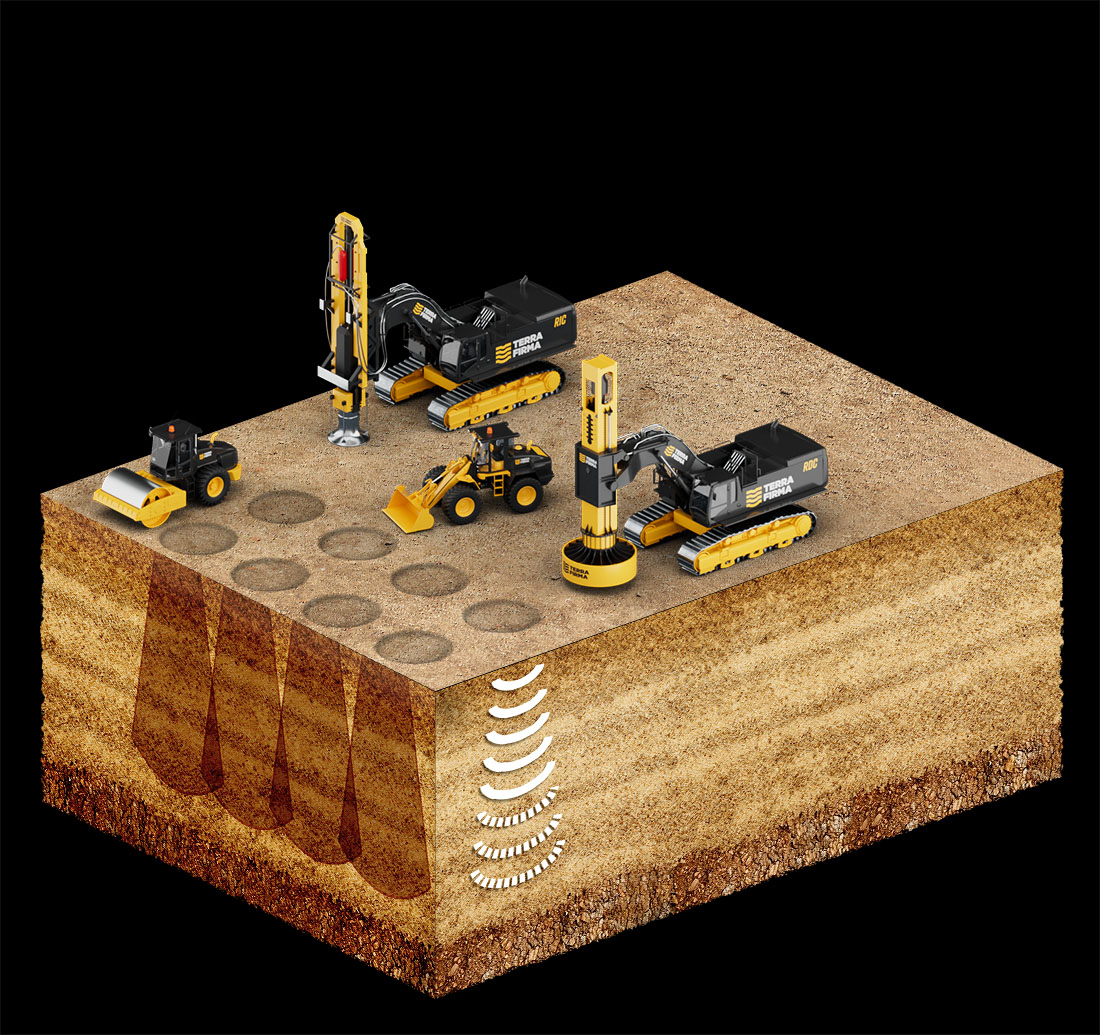
Rapid Dynamic/Impact Compaction (RDC/RIC)
Vibro Compaction (VC)
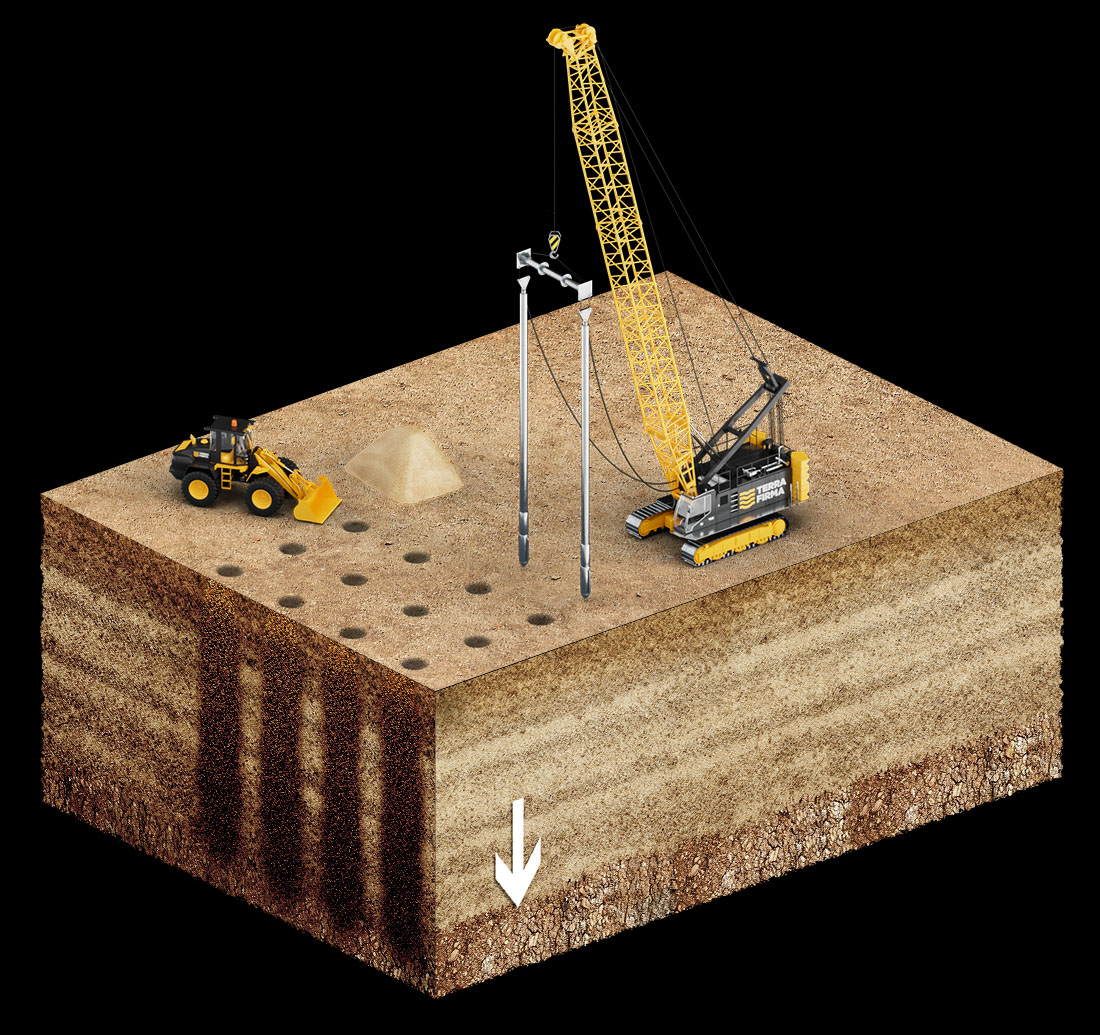
Vibro Replacement (VR)

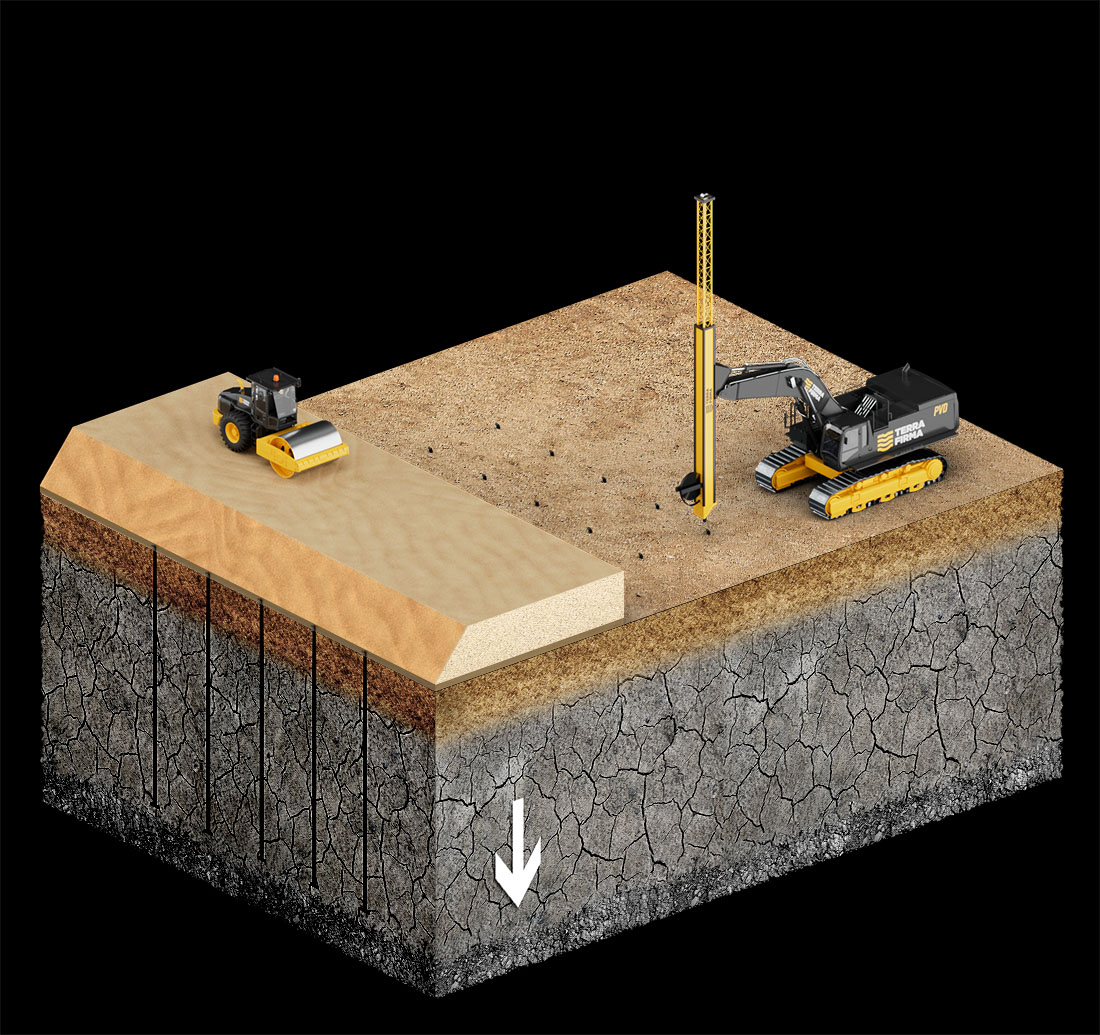
Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVD)

Dynamic Compaction (DC)
Dynamic Compaction (DC) is a Ground Modification technique whereby loose soils can be effectively and economically densified to improve its mechanical characteristics and allow construction of different types of structures without need of deep foundations or soil replacement. The method involves dropping a heavy steel pounders repeatedly on the ground at regularly spaced intervals. The weight and height of pounding depends on the degree of compaction desired. The usual range of pounder is between 10 ton to 33 ton and the drop height can be up to 25m.
Dynamic Compaction (DC) method is applicable for a wide variety of soil conditions including saturated/unsaturated loose Sands, even with the presence of silty pockets, dune sands, inorganic fill, reclaimed soils with variable characteristics and sizes even with presence of large sized boulders, landfills deposits and collapsible soils.
Dynamic Compaction (DC) has been extensively used to compact loose soils to depths of up to 14m, in order to increase the bearing capacity, decrease post construction settlement and mitigate liquefaction risk in case of seismic events.

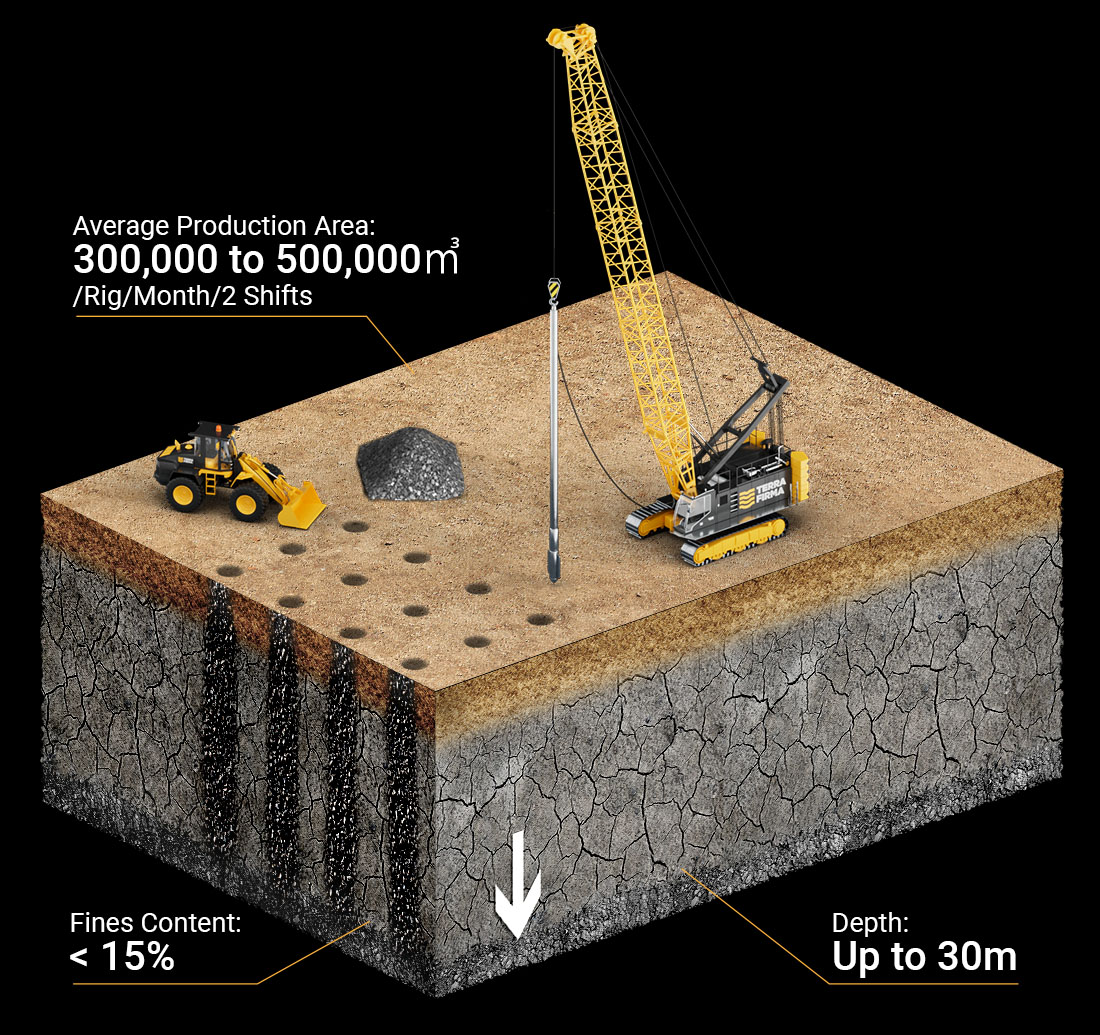
Dynamic Replacement (DR)
Dynamic Replacement (DR) technique is an extension of Dynamic Compaction (DC) to compressible soils (such as soft clays, silt, sabkha…) where a large diameter columns (up to 2.5m diameter) of very dense granular materials are constructed by dropping heavy pounders from great heights into the soft soil.
Dynamic Replacement (DR) technique can be implemented as a global treatment or localized only under foundations in order to increase the soil bearing capacity, reduce the total and differential post-construction settlements and mitigation of liquefaction risk.
This method combines the advantages from both Dynamic Compaction and Stone Columns technologies by creating large sized Dynamic Columns with high stiffness and internal shear resistance and overall improvement of mechanical characteristics of the intermediate soil.
A large variety of readily available granular materials may be used for construction of the DR columns. Clean well graded sands may be the most suitable, however, other sources such as dune sands, gravel/sand mix, concrete rubble/crushed gravel mixed with sand etc. may also be successfully used.
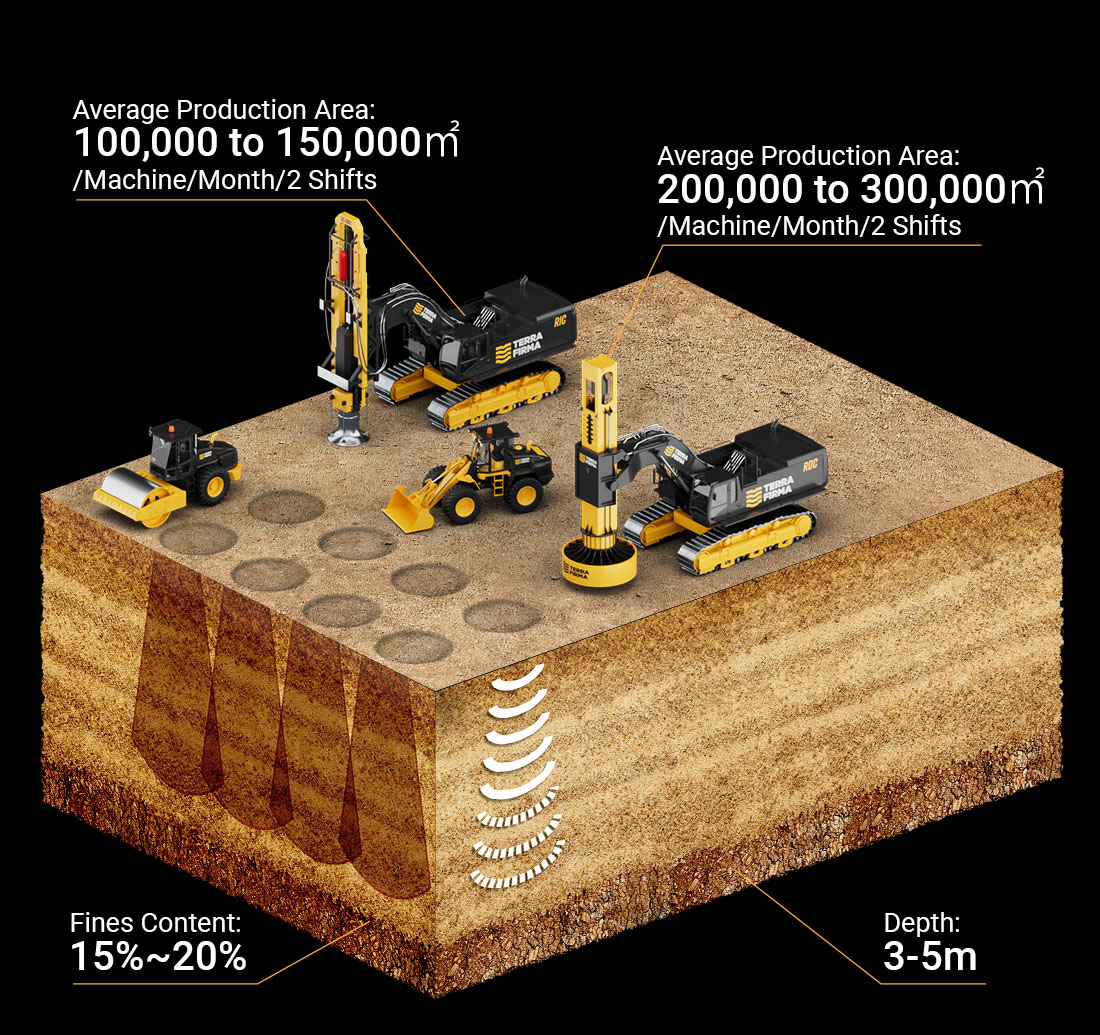
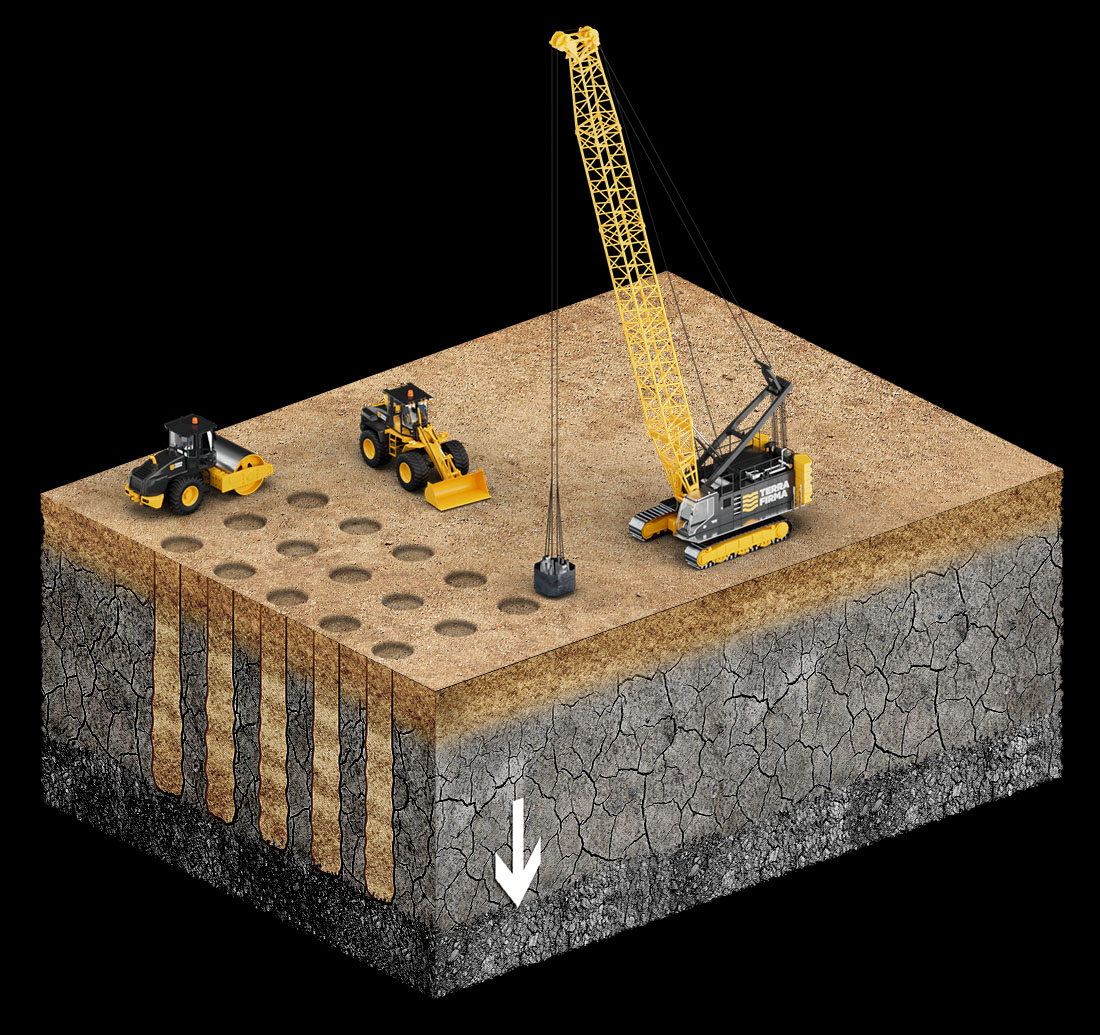
Rapid Dynamic/Impact Compaction (RDC/RIC)
Rapid Dynamic/Impact Compaction (RDC/RIC) technique is a recently developed soil improvement technique, used for compaction of granular soils up to 4-5m deep, as a lighter version of Dynamic Compaction for shallow treatment. The RDC machine consists of a hydraulic excavator base with strengthened arm to which a strengthened arm to which a compaction hammer is attached.
The compaction energy is generated by the fall of a 9-16 ton hammer from height of up to 1.5 m. The hammer falls on a compaction foot having a diameter ranging from 1.5 to 2.6 m, in contact with the ground and the energy is in turn transferred to the ground.
The compaction of the subsoil is initiated by the vibrations generated by the impact of the weight upon the foot, and by the movement of the foot into the ground pushing the material into a denser structure. RDC/RIC technique is well adapted to be used in combination with dynamic compaction, Dynamic Replacement and vibro dynamic compaction techniques in order to improve the surface soil.
RDC/RIC technique generates limited vibrations comparing to dynamic compaction technique and thus can be used close to existing structures.

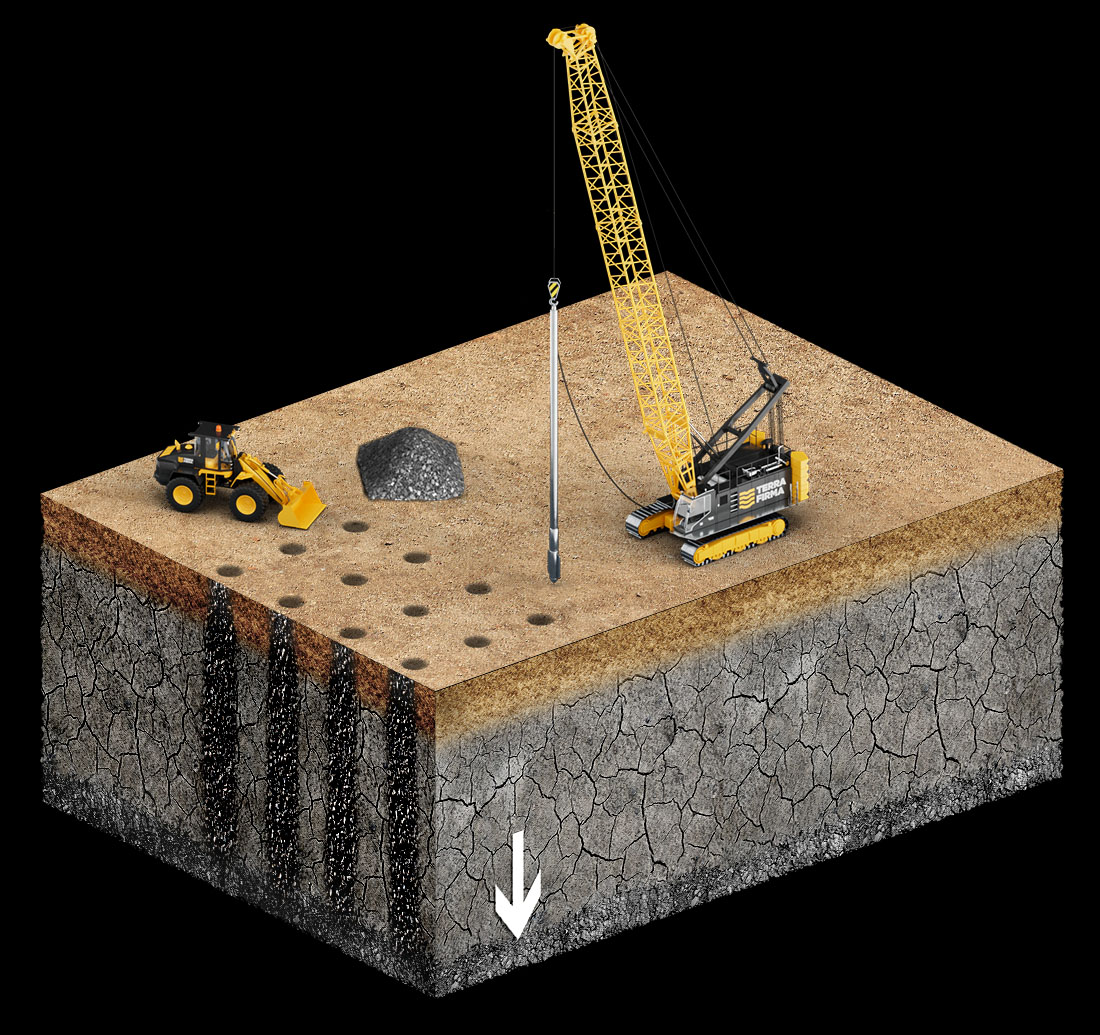
Vibro Compaction (VC)
Vibro compaction is a technique that is applied to compact cohesionless soils with fine content not more than 12%. This process is done using a vibrator that penetrates the ground by means of vibrations and high-pressure water jetting to the desired depth. When the desired depth is reached, the compaction process starts by holding the vibrator in its position for a certain time (usually within 30 seconds) then it is pulled a short distance and held again until reaching the ground surface. The vibrations and the water pressure result in the liquefaction of the cohesionless soil around the vibrator losing the friction between the soil particles and reorienting the particles in denser state and extending the influence of compaction all around the compaction point,
Since the compaction results in reducing the voids within the soil, a depression is observed at the position of the compaction point as a cone-shaped.
Productivity of the vibro compaction can reach 250 lm/shift.

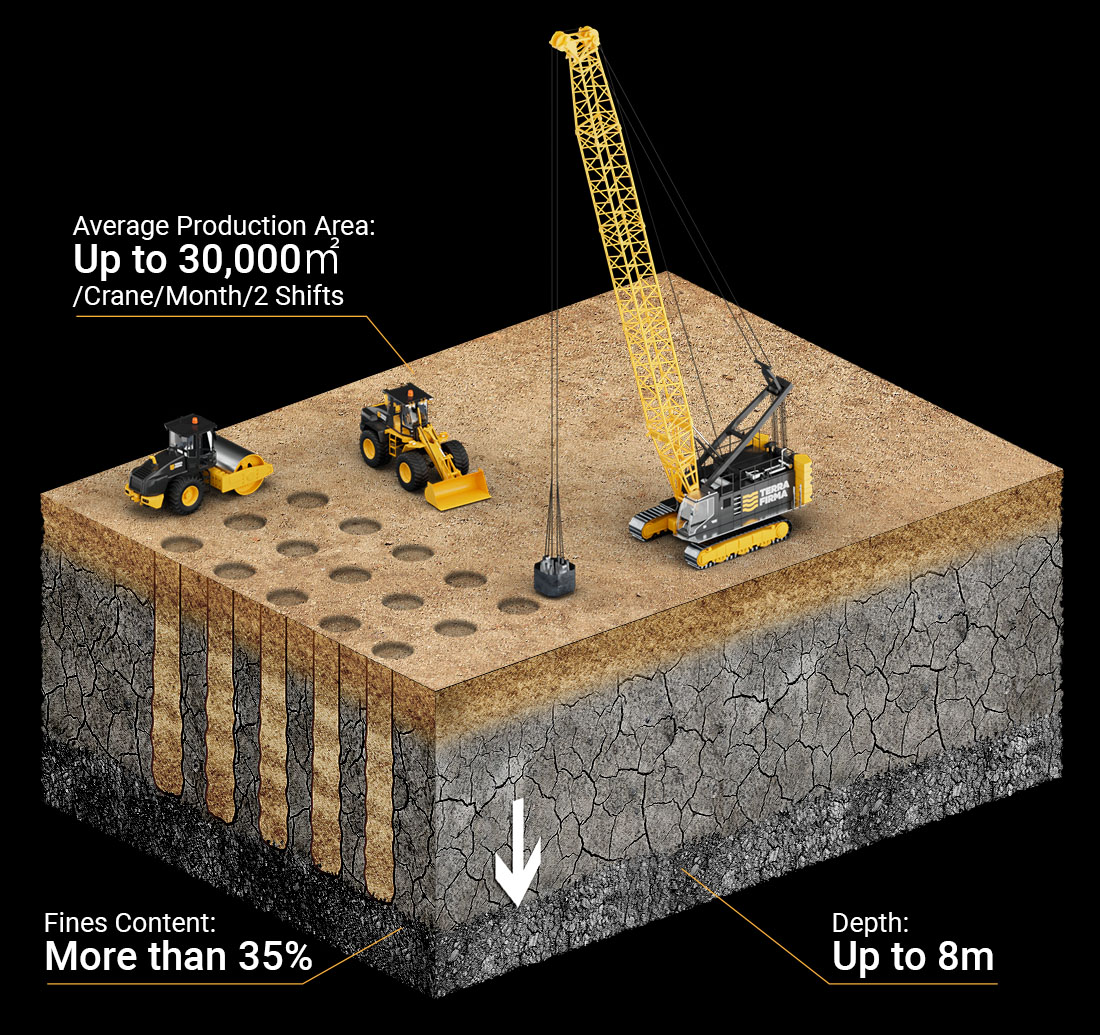
Vibro Replacement (VR)
Vibro Replacement technique which involves the replacement of the fine-grained soil. It is also known as Vibro Stone Columns. During Vibro Replacement, a vibrating probe is inserted into the soil and moved up and down to create a hole. Stone or other suitable material is then introduced into the hole as the probe is gradually withdrawn. The process is repeated until the designed number of stone columns have been installed to improve the soil strength, load-bearing capacity and mitigate liquefaction.
Vibro Replacement is executed by Wet top feed method or Dry bottom feed methods.
In Wet top feed method, the Vibro-Probe is hung from a crane and penetrates to the treatment depth under its own weight, vibratory force and water jetting. The densification and reinforcement process is performed from the bottom upward. During the improvement process, jetting water from the Vibro-Probe tip continues to run, causing water to flush to the surface. The flushing water creates a path for the rock backfill placed at the surface to fall to the base of the Vibro-Probe. The Vibro-Probe is raised a few feet allowing rock to fill the void. The Vibro-Probe is then repenetrated into the rock backfill, densifying the rock and forming a compacted stone column and improved in-situ soil rock matrix. This process is repeated upward in intervals until the stone column is constructed to the surface.
In Dry bottom feed method, a specialty built stone feed tube system delivers the rock backfill to the tip of the Vibro-Probe under compressed air. The process of constructing the stone column is similar to the wet top feed method in that the Vibro-Probe is raised in intervals, from the bottom upward, allowing the stone delivered by the tube to fill the void as the stone column is constructed to the surface.
Productivity of the vibro replacement can reach Wet top feed 300 lm/shift & dry bottom feed can reach to 220lm/shift.
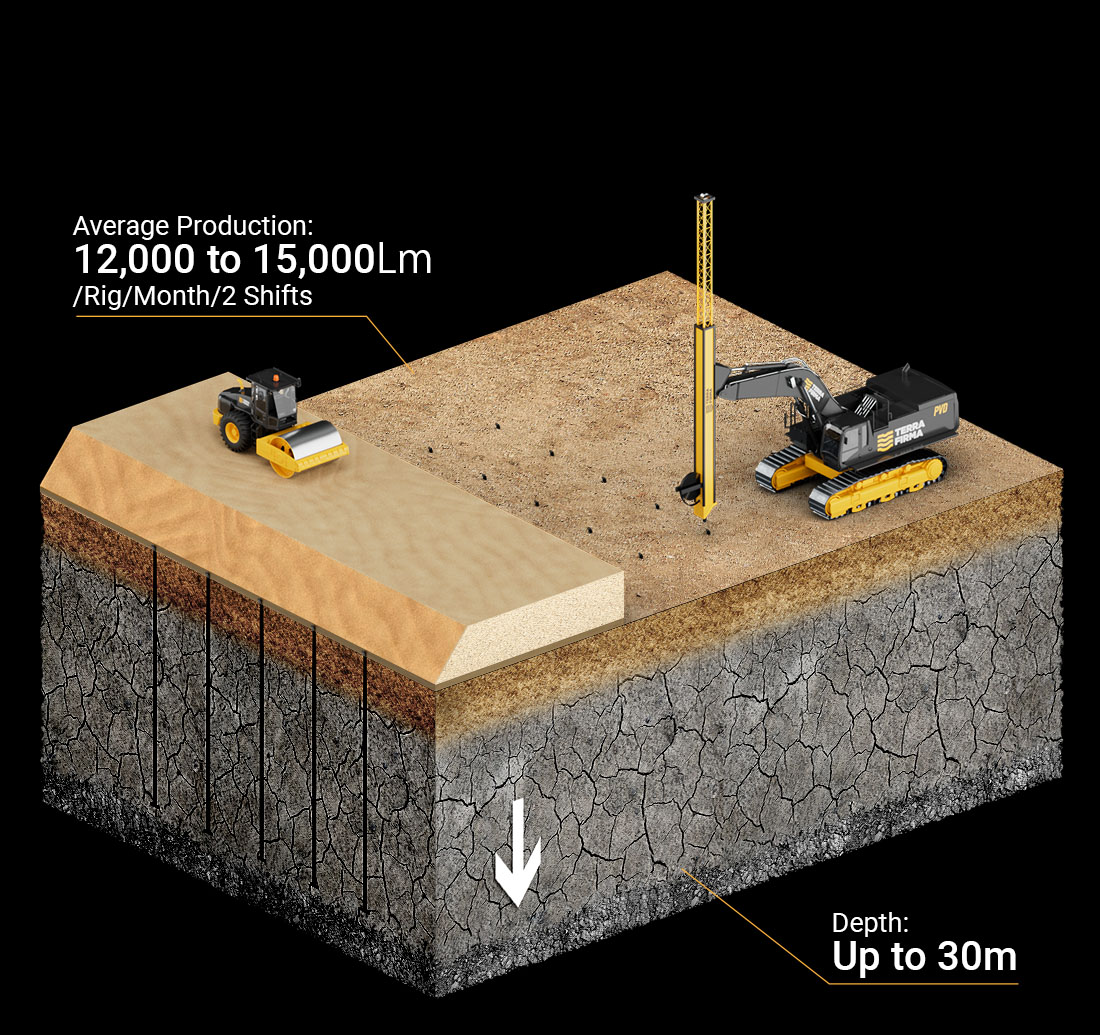
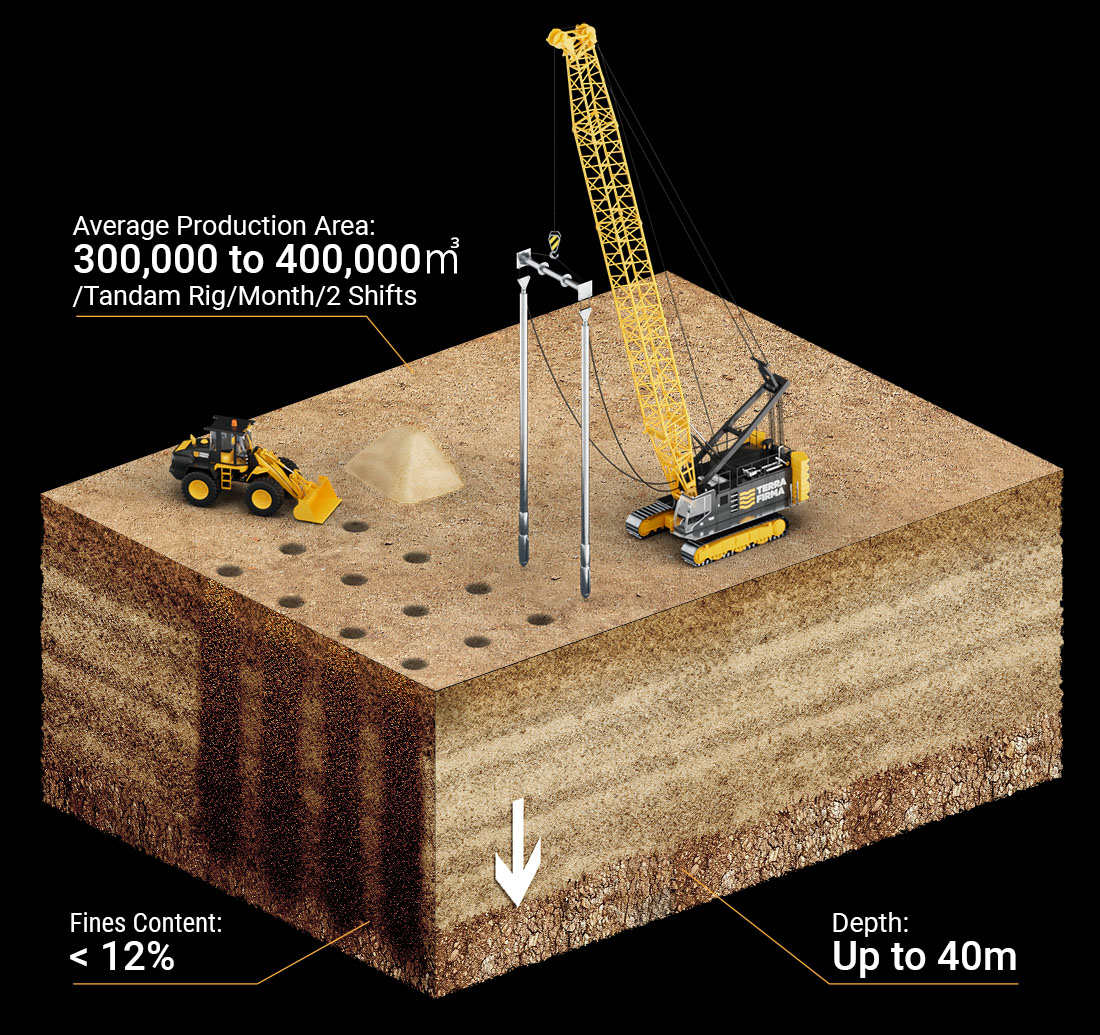
Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVD)
Prefabricated Vertical Drains “PVD” is used as soil improvement technique in soft clay. PVD is composed of a plastic core surrounded by a geotextile filter. The filter is there to avoid clogging of the PVD when installed in soft clay.
The PVD is installed and then followed by preloading surcharge. When PVD is installed, it shortens the drainage path of the water to be half the distance between two PVDs. This combined PVD + preloading solution results in acceleration of the consolidation process which can be observed from the surface settlement of the preloading embankment increase the shear strength of the clay and reducing the residual construction settlement.
different type of instrumentations can be used to monitor the performance of soil improvement using PVD + preloading such as (Surface settlement points, piezometer, extensometers and inclinometers,
Productivity of PVD can reach up to 15,000 lm/shift in favorable conditions.